
Definition of a Project
A project is a temporary endeavor having start-time and end-time, undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.
A project has the following 3 characteristics
Introduction to Project Management
Project Management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to get a ouput in order to meet the requirements of a particular project. Project management is accomplished through the appropriate application and integration of the 49 logically grouped project management processes, which are categorized into 5 Process groups and 10 Knowledge areas
Project management primarily focuses on researching, Initiating, planning, excuting, managing and organizing the available resources. Goal of the project management process have to guide the project team through-out all the phases like Initiation, planning and execution, monitoring, controlling and clossing the project successfully.
Organizational Project Management:
Definition - A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service or result.
Scope - Project have defined objectives, Scope is progressively elobrated throughout the project lifecycle.
Change - Project management team expect change and implement processes to keep change managed and control.
Planning - Project Managers progressively elabrote high - Level information into detailed plans throughout the project lifecycle.
Management - Project manager managing the project team to meet the project objectives.
Monitoring - Project Managers monior and control the work of producing the products, services, or results that the project was under taken to produce.
Success - Success is measured by product and project quality, timelineness, budjet complaince and degree of customer satisfaction.
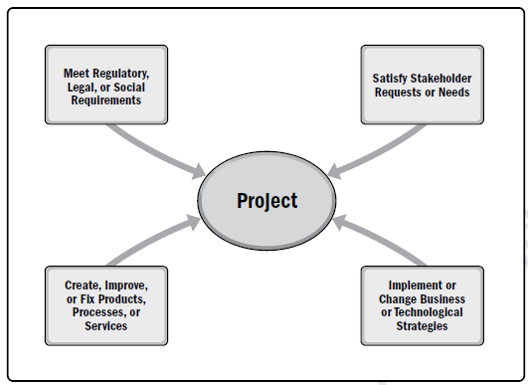
Projects are typically authorized as a result of one or more of the following strategic considerations:
Managing a project typically includes, but is not limited to:
Project enables business value creation. PMI defines business value as the net quantifiable benefit derived from a business endeavor. The benefit may be tangible , intangible or both. In business analysis business value is considered the return, in the form of elements such as time, money, goods or intangibles in return for something exchanged
Project Lifecycle:
A project life cycle includes all the phases required for a project to create a product, service, or result.
The project life cycle is industry specific and can be different for each project.
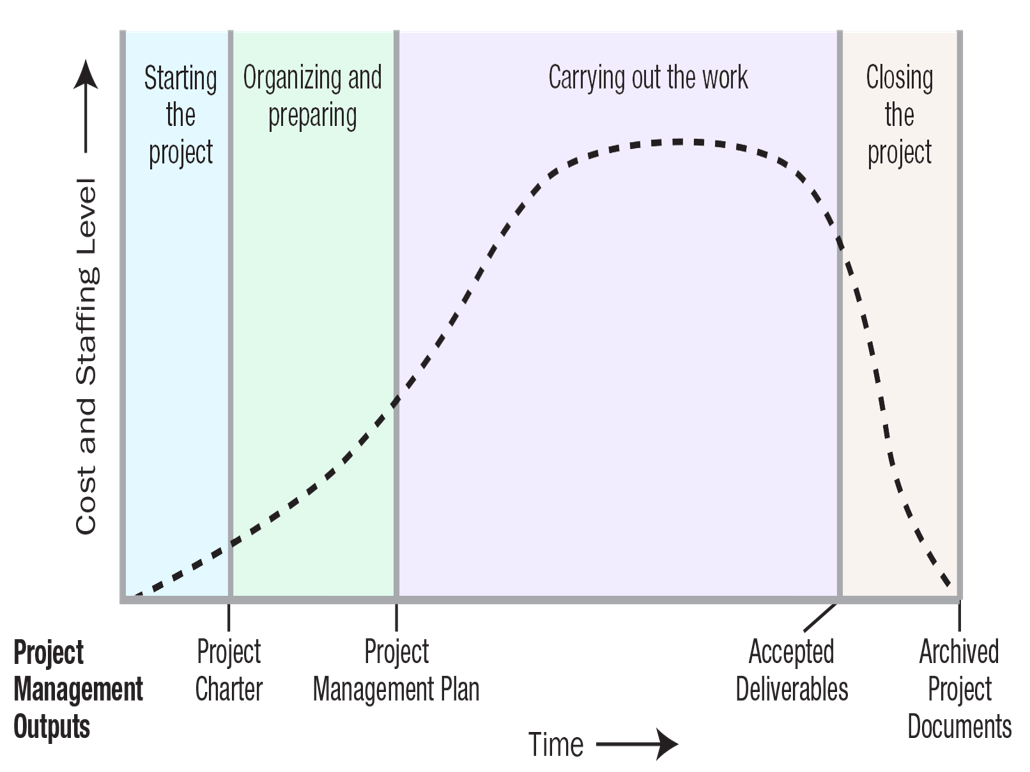
Typical Project Phase – Cost and Staffing Effort
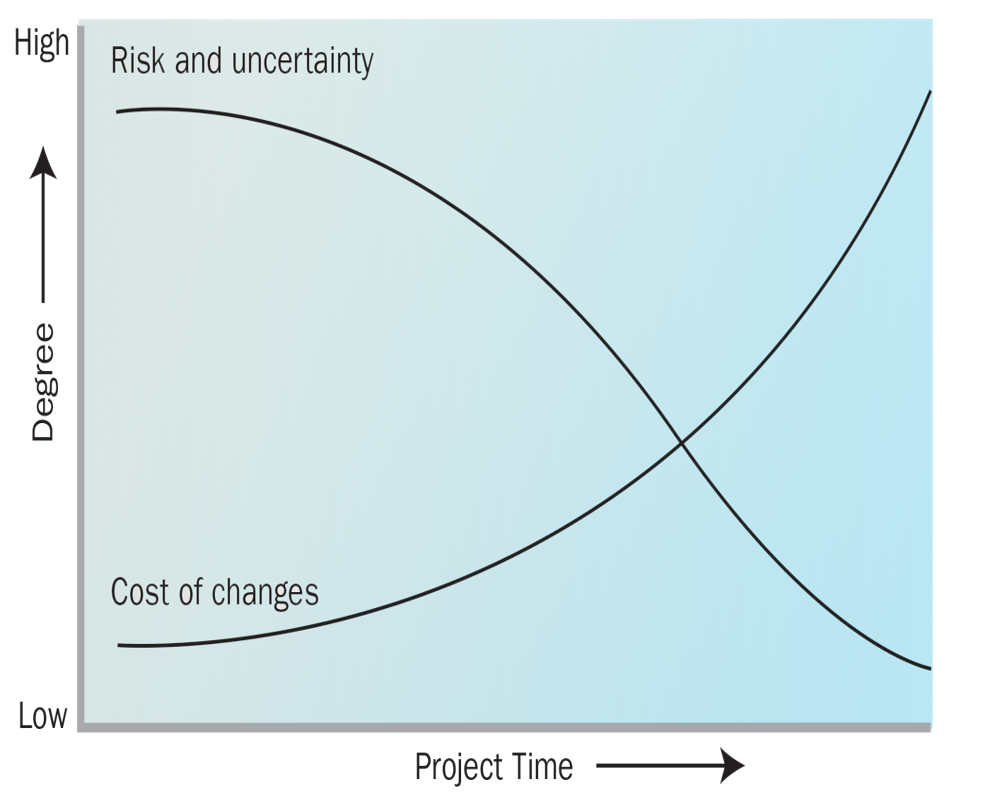
Typical Project Phase – Impact of Changes and Risk
Predictive Life Cycles
Predictive life cycles are ones in which the project scope, and the time and cost required to deliver that scope, are determined as early in the project life cycle as practically possible.
Iterative and Incremental Life Cycles
Iterative and incremental life cycles are ones in which project phases (also called iterations) intentionally repeat one or more project activities as the project team’s understanding of the product increases. Iterations develop the product through a series of repeated cycles, while increments successively add to the functionality of the product.
Adaptive Life Cycles
Adaptive life cycles (also known as change-driven or agile methods) are intended to respond to high levels of change and ongoing stakeholder involvement.
Adaptive methods are also iterative and incremental, but differ in that iterations are very rapid (usually with a duration of 2 to 4 weeks) and are fixed in time and cost.
Product Lifecycle:
A product life cycle defines end to end activities of a product throughout is life cycle
A product life cycle may have several projects (hence multiple project life cycles) and operations.
The product phases are generally sequential and non-overlapping, e.g., a project undertaken to design a new desktop computer is only one phase in the product life cycle.
